Chemiluminescence is the emission of light by molecules, induced by a chemical reaction. A chemiluminescence detector (CLD) is a highly specific GC detector.
Detection principle:
Major components of chemiluminiscence detector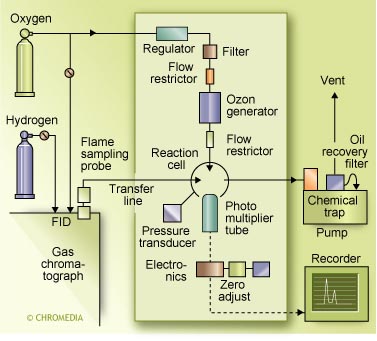
For specific sulphur detection the initial reaction to form the SO-radical is carried out by combustion in a catalytic conversion oven or a hydrogen diffusion flame. Alternatively the flame plasma from a normal FID can be sampled by a suitable probe. Next, a secondary reaction is performed with ozone in an evacuated chamber. The general mechanism for specific sulphur detection is as follows:
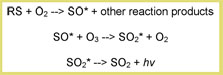
The detection of N-containing species involves a similar suite of reactions.
Sulphur detection by chemiluminescence offers a considerable advantage over the use of the FPD in that the response is equimolar for different compounds, and is intrinsically linear, with a linear response range of >103 and detection limits of 10-12-10-13 g S/s.
Sulfur chemiluminescence detector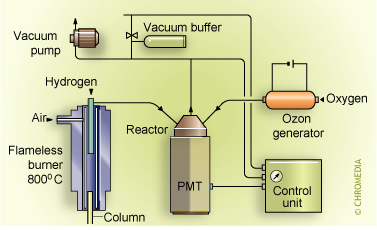
The most important applications for CLD's are for N or S-containing compounds in concentrations as low as the picogram level.
High boiling oil fraction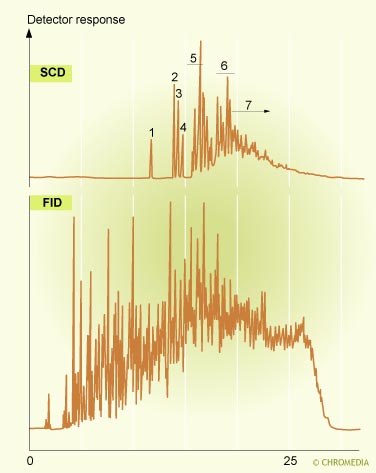
 Did you ever try to explain separation to your employees or students? Well, try no more: Lee Polite did it for you in a way which is hard to beat. We will open up one example of his whiteboard class.
Did you ever try to explain separation to your employees or students? Well, try no more: Lee Polite did it for you in a way which is hard to beat. We will open up one example of his whiteboard class. 




